Below you will find pages that utilize the taxonomy term “Toilets”
Toilets
I thought it would be fun to talk about toilets since we interact with them daily, yet, mostly ignore them and their operation.
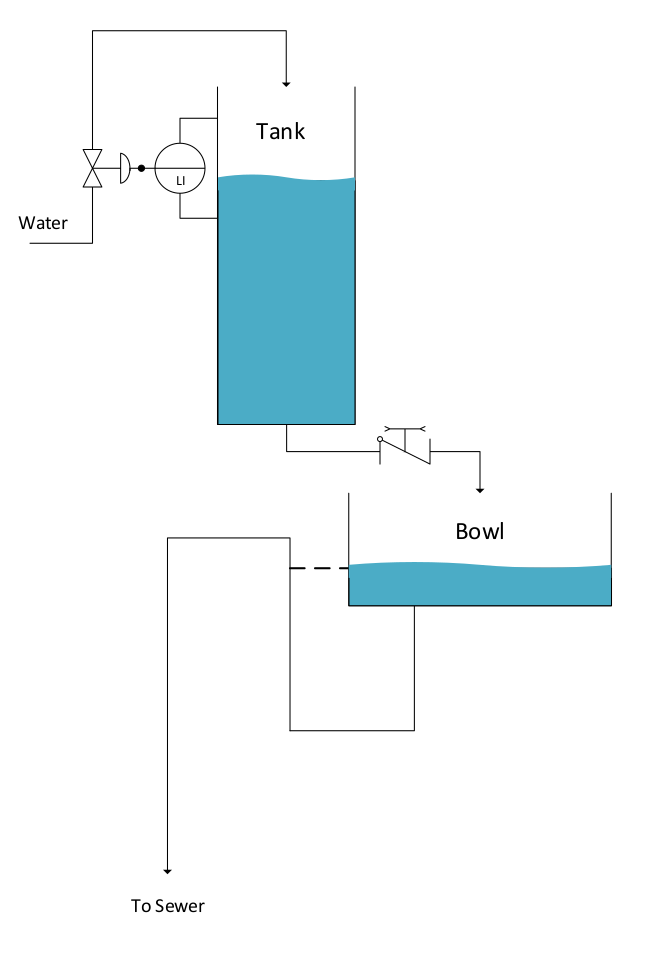
Components:
- water inlet
- diaphragm valve
- Tank open to atmosphere (usually covered)
- Level Indicator with mechanical linkage to diaphragm valve(2)
- Chain operated stop-check valve
- Bowl also open to atmosphere
- S-bend outlet pipe to sewer/septic system
Operation
During normal operation, the water level in the tank is controlled by feedback from the level indicator to the inlet valve. When the level is low, the valve is open filling the tank. When the level is high, the valve is closed. The water level in the bowl is determined by hydrostatic pressure in the s-bend of the outlet pipe. The toilet is flushed by manipulating the check valve releasing water from the tank to the bowl. When the bowl water level exceeds the height of the s-bend, a syphon effect empties both the bowl and the tank. once the check valve is closed, the tank refills to the appropriate level, so the process can be repeated as needed.